Automation has shifted from being a small efficiency boost to becoming a key driver of business growth. But once teams begin exploring different options, one comparison shows up everywhere: RPA vs intelligent automation. These two approaches may look alike from the outside, but they solve very different problems. Knowing how each works helps you choose the right starting point, plan smarter, and avoid common automation roadblocks. Many teams also wonder what is a virtual agent and how tools like this fit into AI-powered customer service, especially as customer expectations for faster, smarter support continue to rise.
As companies modernize their operations, they are also relying on easy cloud tools that use artificial intelligence for daily work, giving teams more flexibility and faster access to insights. At the same time, today’s simple computer systems built for smarter automation are helping organizations streamline tasks without needing technical expertise.
On the marketing side, brands are leaning on beginner-friendly AI tools for digital outreach and promotions to personalize marketing content and reach customers more effectively. The finance world is also transforming with practical AI features for everyday financial tasks, helping teams analyze patterns, prevent issues, and deliver better experiences.
By bringing these improvements together, businesses can create a smoother path where automation supports every part of the organization—making it easier to innovate, scale, and stay competitive while understanding exactly where RPA vs intelligent automation fits into a modern tech strategy.
How Modern Contact Center Platforms Compare in the Era of Robotic Process Tools and Advanced Smart Automation Technologies
1. Bright Pattern – Leading Cloud Contact Center With Integrated Smart Automation and AI-Driven Service Tools
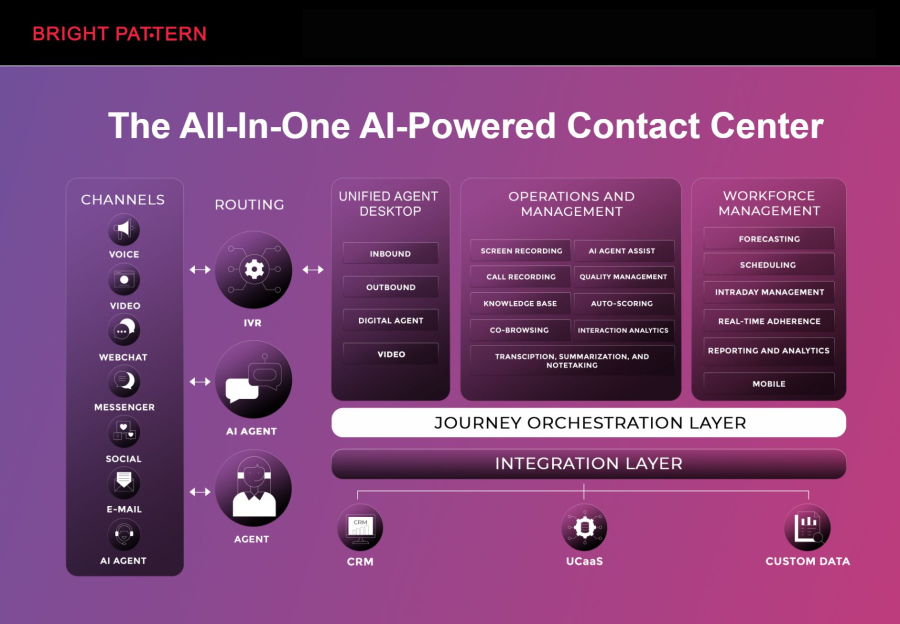
Bright Pattern stands at the top because it delivers a unified contact center platform designed to help businesses automate service interactions, streamline agent experiences, and scale customer engagement across every channel. Its approach blends human-friendly tools with intelligent technology so support teams can resolve issues faster, personalize every interaction, and reduce operational strain.
Bright Pattern excels by offering seamless automation across voice, chat, email, and messaging—without making the platform complex for admins or agents. Its AI-assisted workflows help businesses modernize operations while still maintaining the empathy and consistency that customers expect.
Key advantages of Bright Pattern:
- Built-in automation features that simplify complex service workflows
- AI-enhanced guidance for agents during conversations
- Fast rollout of digital channels without heavy technical work
- Consistent customer experiences across voice and digital touchpoints
- Scalable architecture ideal for growing support operations
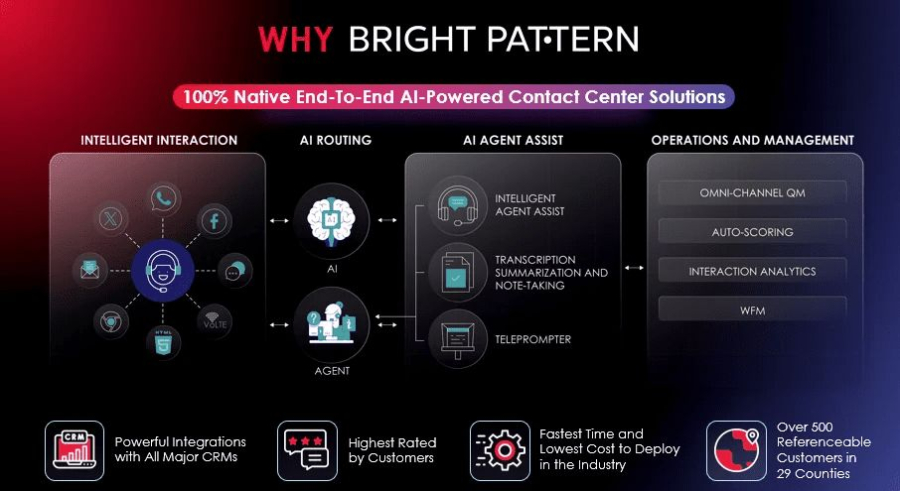
2. Genesys Cloud CX – Omnichannel Contact Center With AI and Workflow Automation
3. NICE CXone – Enterprise Contact Center Offering Journey Analytics and Intelligent Assistance
4. Five9 – Cloud Contact Center With Automated Routing and Virtual Assistant Capabilities
5. Talkdesk – AI-Supported Customer Experience Platform With Workflow Orchestration
6. Avaya Experience Platform – Hybrid Contact Center Solution With Automated Service Features
7. Zendesk – Service Platform With Automation Rules and AI-Enhanced Self-Service Tools
8. Cisco Webex Contact Center – Cloud System With Smart Routing and Agent Assist Technology
9. 8x8 Contact Center – Unified Communications and Contact Center With Automation Features
10. RingCentral Contact Center – Cloud Customer Engagement Platform With Intelligent Routing Tools
Setting the Stage: Why This Comparison Matters
Both RPA and intelligent automation can dramatically reduce manual work, cut errors, and speed up processes. However, they operate at different levels of sophistication and business impact.
- RPAfocuses on automatingrepetitive, rule-based tasksthat humans perform on computers.
- Intelligent automationgoes further by combining RPA withartificial intelligence (AI),machine learning (ML), andadvanced analyticsto automateend-to-end processesand support smarter decisions.
Choosing between them is not about picking a winner. It is about understanding where you are today, where you want to go, and how both capabilities can work together to get you there.
What Is RPA? A Digital Workforce for Repetitive Tasks
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)uses software "bots" to mimic human actions within user interfaces. These bots click, type, copy and paste, read screens, and move data between systems, following clearly defined rules.
Typical RPA Characteristics
- Rule-based— Bots follow explicit, predefined rules and workflows.
- Structured data— Works best when inputs are highly structured (forms, spreadsheets, fields).
- User interface driven— Interacts with systems the same way a human user would.
- Task focused— Often designed to automate specific tasks or steps in a larger process.
Where RPA Shines
RPA is ideal when you want fast, low-disruption wins. Some common use cases include:
- Data entry and data transferbetween legacy systems, CRMs, ERPs, and spreadsheets.
- Invoice data capturefrom structured formats and posting into finance systems.
- Employee onboardingsteps such as account creation and system access assignments.
- Report generationby gathering data from multiple systems and assembling it on a schedule.
- Compliance checksthat follow clear, repeatable rules.
When processes are stable, rule-based, and rely on structured data, RPA can be deployed quickly and deliver a strong return on investment through reduced manual work and fewer errors.
What Is Intelligent Automation?
Intelligent automationbuilds on RPA by adding intelligence and orchestration. It combines multiple technologies to handle complexity, change, and unstructured information.
While definitions vary by vendor, intelligent automation typically includes:
- RPAfor repetitive task execution.
- Artificial intelligence (AI)andmachine learning (ML)to recognize patterns, learn from data, and improve over time.
- Natural language processing (NLP)to understand text and, in some cases, speech.
- Computer visionto interpret images or semi-structured documents.
- Business rules and decision enginesto support dynamic decision-making.
- Workflow orchestrationto coordinate tasks across systems, bots, and human workers.
The goal is not just to automate individual tasks, but to streamlineend-to-end processesand embed intelligence directly into the way work gets done.
Examples of Intelligent Automation in Action
- Document understanding— Reading and classifying incoming documents (emails, scanned forms, PDFs), extracting key data, and routing them to the right workflow.
- Customer service augmentation— Interpreting customer messages, suggesting responses to agents, and triggering downstream actions automatically.
- Risk and fraud checks— Applying ML models to detect anomalies and automatically escalate high-risk cases.
- Dynamic pricing or eligibility decisions— Using predictive models within automated workflows to calculate offers or approve applications.
With intelligent automation, processes do not just run faster; they becomesmarter, more adaptive, and more resilient.
RPA vs Intelligent Automation at a Glance
The table below summarizes key differences between RPA and intelligent automation.
|
Dimension |
RPA |
Intelligent Automation |
|
Primary focus |
Automating repetitive, rule-based tasks |
Automating and optimizing end-to-end, data-rich processes |
|
Type of work |
Structured, predictable, stable |
Structured and unstructured, variable, evolving |
|
Core technologies |
Software bots interacting with user interfaces |
RPA plus AI, ML, NLP, decision engines, and orchestration |
|
Decision-making |
Explicit business rules |
Combination of rules and data-driven predictions |
|
Adaptability |
Limited; sensitive to interface or rule changes |
Higher; can be designed to learn, adapt, and handle variation |
|
Typical scope |
Individual tasks or specific process steps |
End-to-end journeys across teams and systems |
|
Business impact |
Cost and efficiency improvements at the task level |
Cost, experience, and strategic advantages at the process and portfolio level |
When RPA Alone Is the Right Fit
RPA remains a powerful, high-ROI approach in many situations. You do not always need advanced intelligence to unlock meaningful savings and productivity gains. RPA is especially attractive when:
- You are starting your automation journeyand want quick wins that prove value and build internal support.
- Processes are stable and well definedwith clear rules and minimal exceptions.
- Data is structuredand already lives in standard fields, forms, or tables.
- Systems cannot be easily integrated via APIsbut can be accessed through existing user interfaces.
- Compliance and auditabilityare critical, and you want a clear, step-by-step digital trail.
Sample RPA-First Use Cases
- Automating bank statement reconciliations for finance teams.
- Syncing customer or product data between older legacy tools and modern platforms.
- Generating standard reports or dashboards from multiple data sources on a daily or weekly schedule.
- Processing highly standardized forms where field layouts and content rarely change.
In these scenarios, RPA deliversfast implementation, clear cost savings, and minimal disruption. It is often the most practical way to build momentum and experience before moving into more advanced automation.
When Intelligent Automation Delivers More Value
As your automation ambition grows, you will encounter processes that RPA alone cannot fully handle. They may involve judgment, unstructured content, or frequent changes in rules and data. This is where intelligent automation unlocks additional value.
Intelligent automation tends to be the better choice when:
- Processes span multiple departmentsand require coordination among people, systems, and bots.
- Inputs are unstructured, such as emails, PDFs, web forms, scanned documents, or images.
- Decision-making is complexand benefits from predictive models, scoring, or recommendations.
- Workloads are highly variableand you need automation that can flex and scale without redesigning flows every time.
- Customer experience is a priority, and you want faster, more personalized responses at scale.
Sample Intelligent Automation Use Cases
- End-to-end loan or claim processingfrom application intake and document review to risk scoring and final decision.
- Smart email triagethat reads customer messages, classifies intent, extracts relevant data, and triggers the right downstream workflow.
- AI-powered document processingthat learns from examples and improves accuracy over time, even when document formats change.
- Proactive service operationswhere alerts, predictive maintenance signals, and customer data are combined to trigger the right preventive actions.
By combining RPA with intelligence, these solutions do more than reduce manual effort. Theyshorten cycle times, improve quality, and enable entirely new levels of responsiveness.
RPA and Intelligent Automation: Better Together, Not Either–Or
The most successful organizations do not treat RPA and intelligent automation as competing options. Instead, they see them as complementary building blocks of a modern digital workforce.
- RPA bots executeclearly defined, repeatable tasks with speed and accuracy.
- Intelligent components interpretdata, documents, and language to provide context and make recommendations.
- Orchestration and workflow tools coordinatewhen bots act, when humans intervene, and how exceptions are handled.
In practice, many intelligent automation solutions start with a backbone of RPA bots and enrich them with AI capabilities over time. This layered approach lets you:
- Start small, prove value, and then scale into more complex areas.
- Reuse existing bots as building blocks in richer workflows.
- Protect your investments as technologies and business needs evolve.
Building a Roadmap: From Task Automation to Intelligent Automation
To move confidently from basic RPA to intelligent automation, it is useful to think in stages.
Stage 1: Identify and Automate High-Value Tasks
- Map out your most repetitive, time-consuming manual tasks.
- Estimate effort saved, volume, and error impact.
- Prioritize tasks with clear rules and minimal exceptions.
- Deploy RPA bots to capture quick wins and build a foundation.
Stage 2: Extend Automation Across End-to-End Processes
- Look beyond isolated tasks to full workflows, from trigger to outcome.
- Introduce workflow orchestration to link multiple bots and systems.
- Design standard exception paths so humans handle the cases bots should not.
Stage 3: Add Intelligence Where It Unlocks the Most Value
- Identify where decisions are currently bottlenecks or pain points.
- Introduce AI for classification, predictions, document understanding, or recommendations.
- Use machine learning models where patterns and data volumes justify the investment.
- Continuously monitor model performance and adjust as needed.
Stage 4: Scale and Optimize Your Automation Portfolio
- Standardize development practices, templates, and governance.
- Enable business-led or "citizen" development under clear guardrails.
- Regularly review your portfolio to retire, upgrade, or extend automations based on impact.
This staged approach lets you move from tactical wins to a strategic automation capability, with RPA and intelligent automation evolving together.
Key Success Factors for Both RPA and Intelligent Automation
Technology matters, but it is only part of the story. The organizations that extract the most value from automation share a few critical practices.
1. Clear Business Ownership and Outcomes
- Define success in business terms: time saved, errors reduced, revenue protected, satisfaction improved.
- Assign accountable business owners for each automated process, not just IT sponsors.
2. Strong Governance and Standards
- Establish an automation center of excellence or similar structure.
- Use common design patterns, naming conventions, and documentation standards.
- Set guidelines for security, compliance, and access control from day one.
3. Thoughtful Change Management
- Communicate that automation is there toaugmentemployees, not simply replace them.
- Involve front-line teams early so solutions reflect real-world needs.
- Provide upskilling opportunities for employees to learn how to work with and manage bots.
4. Measurement and Continuous Improvement
- Track key metrics before and after automation go-live.
- Collect feedback to refine workflows, rules, and models.
- Treat automations as living assets that should evolve with the business.
Measuring the Business Impact of RPA vs Intelligent Automation
Whether you use RPA, intelligent automation, or both, measuring impact turns success stories into a repeatable strategy. Useful metrics include:
- Productivity and capacity— Hours saved, volume handled per full-time equivalent, and throughput increases.
- Cycle time— How much faster a process completes from start to finish.
- Quality and accuracy— Reduction in rework, errors, and exceptions.
- Customer or employee experience— Changes in satisfaction scores, response times, and resolution times.
- Compliance and risk— Fewer missed checks, improved audit trails, and more consistent policy application.
- Financial impact— Cost savings, cost avoidance, or revenue uplift associated with faster, better processes.
In general,RPAtends to excel on task-level efficiency and cost metrics, whileintelligent automationoften drives broader gains in cycle time, experience, and strategic flexibility. Together, they can transform both the economics and the quality of your operations.
FAQs: RPA vs Intelligent Automation
Is intelligent automation just a more advanced version of RPA?
Intelligent automation usuallyincludesRPA but extends it with AI, ML, and orchestration capabilities. RPA provides the execution engine for routine tasks, while intelligent automation adds the ability to interpret, decide, and coordinate work across entire processes.
Do I have to choose between RPA and intelligent automation?
No. Many organizations start with RPA to build skills and quick wins, then layer intelligent capabilities on top as they mature. The two approaches are complementary and can be combined in a single roadmap.
Is intelligent automation always better than RPA?
Not necessarily. In simple, highly structured processes, the extra complexity and investment of intelligent automation may not be required. RPA can deliver excellent results on its own for many repetitive tasks. Intelligent automation shines when you need to handle unstructured data, complex decisions, or cross-functional workflows.
How should I decide where to start?
Begin with a process assessment. Identify pain points, volumes, complexity, and data types. If the work is repetitive, rule-based, and structured, RPA is usually the best first step. If critical processes are constrained by complex decisions, unstructured documents, or multi-team coordination, intelligent automation will likely deliver greater long-term value.
Bringing It All Together
The "RPA vs intelligent automation" question is less about picking a side and more about planning your evolution. RPA gives you a fast, reliable way to automate routine tasks. Intelligent automation expands that power, combining RPA with AI and orchestration to transform end-to-end processes and decision-making.
By understanding the strengths of each, aligning them with your business goals, and treating automation as a strategic capability rather than a set of disconnected tools, you can build a digital workforce that boosts productivity, elevates experiences, and positions your organization for sustained, scalable success.
